Managing Window Input Focus
Learn how to manage and control window input focus in SDL applications, including how to create, detect, and manipulate window focus states.
This legacy content uses SDL2
An updated version using SDL3 is available
On most platforms, multiple applications can be open at once. However, when the user is providing input on their keyboard, they typically only intend to provide that input to one of the open applications.
Users can select which application is active by, for example, clicking within its window.
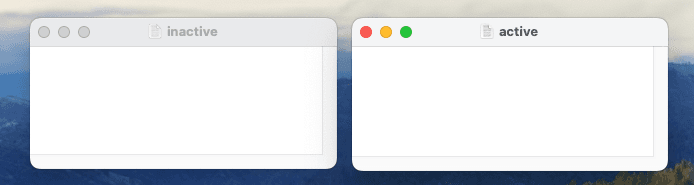
Operating systems typically apply more vibrant styling to the active window. In the following example, the left window is inactive, while the right is active.
Accordingly, the user will not expect the left window to react to keyboard events, as their input is likely intended for the right window instead:
Creating a Window with Input Focus
The SDL_WindowFlags mask includes a bit dedicated to whether or not the window has input focus. The SDL_WINDOW_INPUT_FOCUS variable is available to represent this bit.
Accordingly, we can specify that our window should have input focus as soon as it is created by using this variable with SDL_CreateWindow():
// Window.h
#pragma once
#include <SDL.h>
class Window {
public:
Window(){
SDLWindow = SDL_CreateWindow(
"Hello Window",
100, 100, 700, 300,
SDL_WINDOW_INPUT_FOCUS
);
}
// ...
private:
SDL_Window* SDLWindow{nullptr};
// ...
};We can combine SDL_WINDOW_INPUT_FOCUS with other window flags using the | operator. For example, to create a window that is both resizable and grabs focus when created, we could use this:
SDL_CreateWindow(
"Hello Window", 100, 100, 700, 300,
SDL_WINDOW_INPUT_FOCUS | SDL_WINDOW_RESIZABLE
);Bitwise Operators and Bit Flags
Unravel the fundamentals of bitwise operators and bit flags in this practical lesson
Detecting if a Window has Input Focus
SDL keeps the window flags bitset up to date through the lifecycle of our program. We can get the current window flags at any time using the SDL_GetWindowFlags() function. We pass the pointer to our window - that is, the SDL_Window* value returned from SDL_CreateWindow():
SDL_GetWindowFlags() returns a bit mask in the form of a Uint32 (a 32-bit unsigned integer):
#include <iostream>
#include <SDL.h>
#include "Window.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO);
Window GameWindow;
SDL_Event Event;
std::cout << "Window Flags: "
<< SDL_GetWindowFlags(GameWindow.SDLWindow);
while (true) {/*...*/}
SDL_Quit();
return 0;
}Window Flags: 516We can use the value returned by this function with the & operator to determine if any flag is currently set, Below, we use this technique to determine if the window currently has input focus:
#include <iostream>
#include <SDL.h>
#include "Window.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO);
Window GameWindow;
SDL_Event Event;
Uint32 Flags{
SDL_GetWindowFlags(GameWindow.SDLWindow)};
if (Flags & SDL_WINDOW_INPUT_FOCUS) {
std::cout << "Window has input focus";
}
while (true) {/*...*/}
SDL_Quit();
return 0;
}Window has input focusUsing SDL_GetKeyboardFocus()
Alternatively, we can determine which window currently has focus using the GetKeyboardFocus() function:
#include <iostream>
#include <SDL.h>
#include "Window.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO);
Window GameWindow;
SDL_Event Event;
std::cout << "Window with focus: "
<< SDL_GetKeyboardFocus();
while (true) {/*...*/}
SDL_Quit();
return 0;
}Window with focus: 0000022391741BF8This returns a SDL_Window*, which we can compare to any other SDL_Window* to understand whether or not it has focus:
#include <iostream>
#include <SDL.h>
#include "Window.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO);
Window GameWindow;
SDL_Event Event;
SDL_Window* Focused{SDL_GetKeyboardFocus()};
if (Focused == GameWindow.SDLWindow) {
std::cout << "GameWindow has input focus";
}
while (true) {/*...*/}
SDL_Quit();
return 0;
}GameWindow has input focusUsing the Event Loop
We can also keep track of whether or not our window has focus using the event loop. When our window gains or loses focus, SDL broadcasts an SDL_WINDOWEVENT.
To determine whether the event was caused by a window gaining or losing input focus, we can compare the Event.window.event property to SDL_WINDOWEVENT_FOCUS_GAINED and SDL_WINDOWEVENT_FOCUS_LOST constants respectively:
#include <iostream>
#include <SDL.h>
#include "Window.h"
void HandleWindowEvent(SDL_WindowEvent& E) {
if (E.event == SDL_WINDOWEVENT_FOCUS_GAINED) {
std::cout << "Window gained input focus\n";
}
if (E.event == SDL_WINDOWEVENT_FOCUS_LOST) {
std::cout << "Window lost input focus\n";
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO);
Window GameWindow;
SDL_Event Event;
while (true) {
while (SDL_PollEvent(&Event)) {
if (Event.type == SDL_WINDOWEVENT)
HandleWindowEvent(Event.window);
}
}
SDL_Quit();
return 0;
}Window gained input focus
Window lost input focus
Window gained input focusGrabbing Input Focus
When we want input focus to shift to our application, we can use the SDL_RaiseWindow() function, passing a pointer to our SDL_Window:
SDL_Window* MyWindow{GameWindow.SDLWindow};
SDL_RaiseWindow(MyWindow);In addition to grabbing focus, SDL_RaiseWindow() will also move the window to be in front of any other windows that might be obscuring it. This ensures the user is aware that it has taken focus, and will now be handling their input.
In the following example, our window automatically grabs input focus 5 seconds after it loses it. Window events have a windowID property, representing which window caused the event. We can pass this ID to the SDL_GetWindowFromID() function to retrieve the SDL_Window* associated with that ID:
#include <iostream>
#include <SDL.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
#include "Window.h"
void HandleWindowEvent(SDL_WindowEvent& E) {
if (E.event == SDL_WINDOWEVENT_FOCUS_GAINED) {
std::cout << "Window gained input focus\n";
}
if (E.event == SDL_WINDOWEVENT_FOCUS_LOST) {
std::cout << "Window lost input focus\n";
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(5s);
SDL_RaiseWindow(SDL_GetWindowFromID(E.windowID));
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {/*...*/}
Window gained input focus
Window lost input focus
Window gained input focusSummary
In this lesson, we explored how to manage window input focus using SDL. The key takeaways include:
- Creating windows with input focus using
SDL_CreateWindow(). - Detecting if a window has input focus using
SDL_GetWindowFlags()andSDL_GetKeyboardFocus(). - Handling window focus events in the event loop.
- Using
SDL_RaiseWindow()to grab input focus and bring the window to the front. - Understanding the limitations of
SDL_SetWindowInputFocus(). - Reacting to keyboard events when the window has input focus.
Understanding Keyboard State
Learn how to detect and handle keyboard input in SDL2 using both event-driven and polling methods. This lesson covers obtaining and interpreting the keyboard state array.