Window Decorations and Borders
An introduction to managing SDL3 window decorations, borders, and client areas.
As we've likely noticed, platforms typically add decorations to our windows, such as a title bar and borders. But what if you need a clean, borderless look?
In this lesson, we'll cover everything you need to know about customizing SDL3 window styles, including removing decorations and dynamically adding them back.
The following screenshot is from Windows 11. It shows a decorated window on the left and an equivalent window without those decorations on the right:
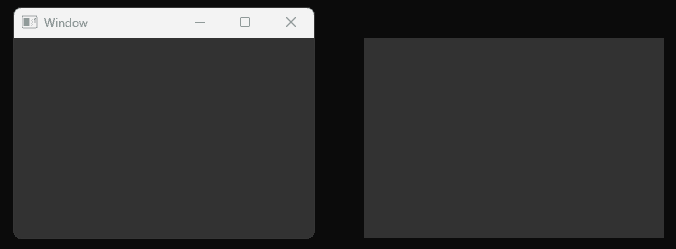
SDL refers to these decorations as borders but, as we can see above, they can also include things like the title bar on desktop platforms.
Starting Point
This lesson builds on our earlier work. To focus on window borders, we will start with a minimal project containing a Window class and a main function with a basic application loop:
Files
Creating a Borderless Window
By default, SDL asks the platform to include these decorations for our window. We can opt to exclude them by passing the SDL_WINDOW_BORDERLESS window flag to SDL_CreateWindow():
src/Window.h
#pragma once
#include <SDL3/SDL.h>
class Window {
public:
Window() {
SDLWindow = SDL_CreateWindow(
"My Program", 600, 300,
SDL_WINDOW_BORDERLESS
);
}
// ...
};Running this code will produce a clean, undecorated window.
Adding and Removing Borders
We can add or remove decorations from an existing window using the SDL_SetWindowBordered() function. We pass the SDL_Window pointer as the first argument, and true or false as the second argument.
Let's add a SetBordered() method to our Window class to encapsulate this functionality:
src/Window.h
#pragma once
#include <SDL3/SDL.h>
class Window {
public:
// ...
void SetBordered(bool Bordered) {
SDL_SetWindowBordered(GetRaw(), Bordered);
}
// ...
};Now we can toggle the border from our main function. For example, we could remove the border when the 'B' key is pressed:
src/main.cpp
#include <SDL3/SDL.h>
#include <SDL3/SDL_main.h>
#include "Window.h"
int main(int, char**) {
SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO);
Window GameWindow;
SDL_Event Event;
bool IsRunning = true;
while (IsRunning) {
while (SDL_PollEvent(&Event)) {
if (Event.type == SDL_EVENT_KEY_DOWN &&
Event.key.key == SDLK_B) {
GameWindow.SetBordered(false);
} else if (Event.type == SDL_EVENT_QUIT) {
IsRunning = false;
}
}
GameWindow.Render();
GameWindow.Update();
}
SDL_Quit();
return 0;
}We can check if a window currently has borders by retrieving its flags with SDL_GetWindowFlags() and testing if the SDL_WINDOW_BORDERLESS flag is set. Let's add an IsBorderless() helper to our Window class:
src/Window.h
#pragma once
#include <SDL3/SDL.h>
class Window {
public:
// ...
bool IsBorderless() const {
return (SDL_GetWindowFlags(GetRaw()) &
SDL_WINDOW_BORDERLESS) != 0;
}
// ...
};We can now use this method to check the window's state:
src/main.cpp
#include <SDL3/SDL.h>
#include <SDL3/SDL_main.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "Window.h"
int main(int, char**) {
SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO);
Window GameWindow;
GameWindow.SetBordered(false);
if (GameWindow.IsBorderless()) {
std::cout << "Window is borderless\n";
}
GameWindow.SetBordered(true);
if (!GameWindow.IsBorderless()) {
std::cout << "Not any more!";
}
// ... (rest of the main function)
}Window is borderless
Not any more!Client Area and Border Size
When setting the position or size of a window in SDL, we are defining the dimensions of the client area. The client area is the region of the window where the application's content is displayed, excluding any decorations like the title bar or window borders.
Decorations are added outside the client area. For instance, if you specify a window height of 200, the client area will be exactly 200 points tall, but the total window height will also include the additional space occupied by decorations.
To precisely control the overall window size or position, it's important to account for the size of these decorations.
The SDL_GetWindowBordersSize() function can help us here. We pass the SDL_Window pointer and four integer pointers. The integers will be updated with the size of the decorations on the top, left, bottom, and right of our window respectively:
src/main.cpp
#include <SDL3/SDL.h>
#include <SDL3/SDL_main.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "Window.h"
int main(int, char**) {
SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO);
Window GameWindow;
int Top, Left, Bottom, Right;
SDL_GetWindowBordersSize(
GameWindow.GetRaw(),
&Top, &Left, &Bottom, &Right
);
std::cout << "Top: " << Top
<< ", Left: " << Left
<< ", Bottom: " << Bottom
<< ", Right: " << Right << '\n';
// ... (rest of the main function)
}Top: 31, Left: 8, Bottom: 8, Right: 8We can pass a nullptr for any of these arguments to ignore the decoration size on that side. For example, passing nullptr for the left and right pointers will only return the sizes of the top and bottom decorations.
// We only care about the top and bottom decoration size
int Top, Bottom;
SDL_GetWindowBordersSize(
GameWindow.GetRaw(),
&Top,
nullptr,
&Bottom,
nullptr
);This function returns 0 if successful, or a negative error code otherwise. We can call SDL_GetError() for an explanation of the error, a technique covered in our lesson on .
int Top;
int ExitCode = SDL_GetWindowBordersSize(
nullptr, &Top, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
if (ExitCode < 0) {
std::cout << "Error getting border size: "
<< SDL_GetError();
}Error getting border size: Invalid windowSummary
In this lesson, we introduced window decorations and how to control them. This included making windows borderless and measuring their decorations for precise layout control.
Key Takeaways
- SDL provides the
SDL_WINDOW_BORDERLESSflag to create borderless windows. - Use
SDL_SetWindowBordered()to dynamically toggle decorations. - The
SDL_GetWindowBordersSize()function helps calculate the size of window decorations.
Window Titles
Learn how to set, get, and update window titles dynamically